Introduction
TCP, full named as Transmission Control Protocol, is a connection-oriented protocol, which means that it requires handshaking to set up end-to-end communications. Once a connection is set up, user data may be sent bi-directionally over the connection.
UDP, full named as User Datagram Protocol, is a simpler message-based connectionless protocol. Connectionless protocols do not set up a dedicated end-to-end connection. Communication is achieved by transmitting information in one direction from source to destination without verifying the readiness or state of the receiver.
They are both connection layer protocol based on IP.
The TCP’s features:
TCP’s State, three-way handshake, error detection, visit Protocal operation for detail!
Comparison
Comparison Chart: TCP vs. UDP
Features: Comparison of UDP and TCP
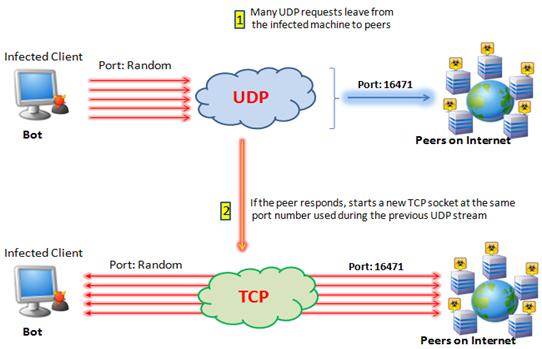
from Internet
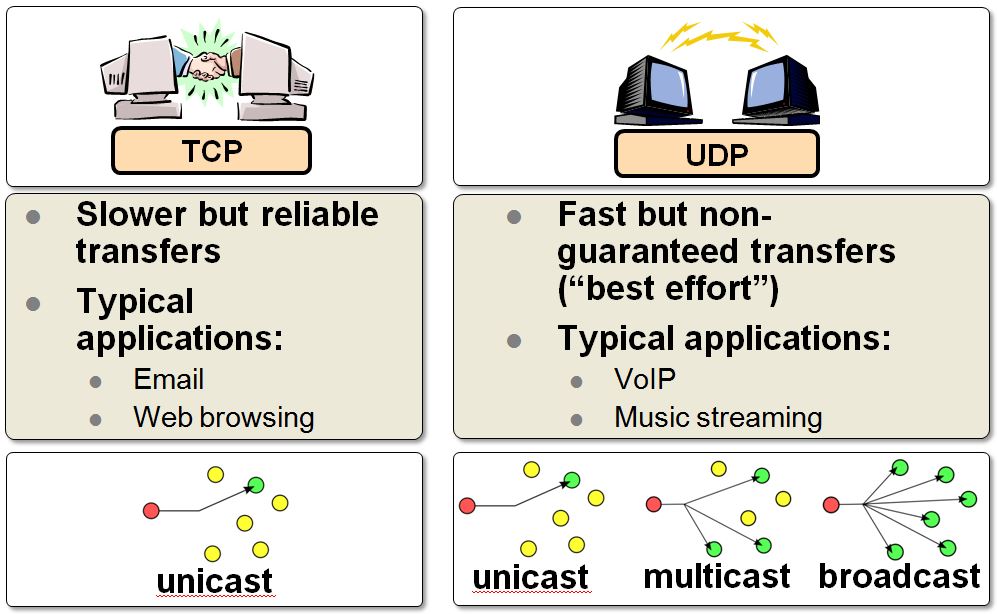
from Internet
Why Different?
Three-way hanshake, windowing, sequence numbering, error detection and recovery - are strictly TCP features. UDP doesn’t use any of them.
Why doesn’t UDP offer these features?
Answer is the Header difference of TCP & UDP.
Take a look at TCP Header - Wikipedia & UDP Header - Wikipedia, then we could know TCP Header is more implicit than UDP’s.
The UDP header has no sequence number field, no ack number field, no ACK bit, n SYN bit, and no windoen field.
The TCP and UDP header have only three values in common - the source port, the destination port, and the checksum.
That’s Why TCP could offer more these features but UDP can’t offer them.
Why in the world do we use UDP for anything?
- The TCP header is much larger than the UDP header. That header is being applied to every segment, and that adds up. UDP’s advantage over TCP is that its header is much smaller than TCP’s.
Applications
The applications of TCP & UDP are based on their features & your real business scenarios.
UDP
Used by DNS,SNMP, RIP, DHCP and etc..
Numerous key Internet applications use UDP, such as DNS - where queries must be fast and only consit of a single followed by a single reply packet, SNMP, RIP and DHCP.
Voice and video traffic is generally transmitted using UDP. Real-time video and audio streaming protocols are designed to handle occasional lost packets, so only slight degradation in quality occurs, rather than large delays if lost packets were retransmitted.
TCP
Used by SMTP, TELNET, HTTP, FTP and etc..
TCP is used extensively by many applications available by internet, including the World Wide Web (WWW), E-mail, File Transfer Protocol, Secure Shell, peer-to-peer file sharing, and streaming media applications.
End by Robin on February 14, 2017 at Office
It’s Valentine’s Day!