
在这几天对 CSS in JS 的学习、研究及若干实践之后…
SUMMARY/总结
- 首先要明白的是: Style != CSS,样式处理的核心应该是外观(What Look like)。
- 结合 JS 的特点,使用 JS 语言的能力或许能够更好地处理好“外观”。
- 应该根据实际应用场景来制定“外观”处理策略,寻找特定 best practise。
- 基于 React 的应用场景来说,如果应用于 跨桌面端浏览器、跨版本之下的话,React 还是依赖于某些特定的 CSS 库,这种情况下,React 采用 LESS 的写法能有更好地兼容性。
CSS in JS 分水岭
2014年11月,Christopher Chedeau 在 NationJS 谈了React: CSS in JS(Stats: 753,383 Views),这个 slide 介绍了 CSS 在项目开发中存在的问题及其解决方式,同时举例了 JS 下的解决方法,成为了一个重要分水岭。从此,React Style,jsxstyle、Radium、CSS Module等陆续出现,大大提高了 CSS in JS 的各种实现可能。
CSS in JS 需要解决的问题:
- JS 下如何实现
:hover,:focusand:active。 - 媒体查询(Media Queries)。
- CSS 动画(Keyframes animation)。
- 等等…
这个视频提出的方案,能够较好的解决 CSS 在 JS 中使用会遇到的问题:Michael Chan - Inline Styles: themes, media queries, contexts, & when it’s best to use CSS
CSS in JS 的相关库
CSS in JS 的优势
- 命名冲突:避免 CSS 命名冲突,解决原生 CSS 有隔离问题。
- 组件独立:实现组件源代码独立。
- JS 能力:可以使用 JS 能力进行事件流、计算、逻辑判断等。
CSS in JS 的弊端
- 代码维护难度增加(maintenance):JS 业务逻辑代码中与样式代码杂糅在一块,耦合性增加,让代码更难以阅读和维护。
- 开始调试难度增加(debugging):在 Inspector 对列表
<ul>的 item 的改样式时,改动只能作用到一项<li>中。 - 降低了样式复用性(re-usability):耦合性与 JS 样式片段不通用所致。
- 覆写样式变得复杂(override styles): 使用 Inline Style 之后,重写覆盖变得困难,需要像 Material-UI 一样,预留 Theme.set() 接口。同时,也可能需要
Object.assign()函数来合并style={}中的各个 JS 样式 ohject。 - JS 性能损失(performance loss):JS 用于计算样式导致了性能损失。
React 官方对 Inline Style 的 介绍
可以说,React 官方对 Inline Style 是持支持态度的,并将可能在未来 React 版本中提供更好的支持。
React 下,Inline Style 写法如下:
var divStyle = {
color: 'white',
backgroundImage: 'url(' + imgUrl + ')',
WebkitTransition: 'all', // note the capital 'W' here
msTransition: 'all' // 'ms' is the only lowercase vendor prefix
};
ReactDOM.render(<div style={divStyle}>Hello World!</div>, mountNode);
说明:
- 采用驼峰(camelCased)写法,对于
backgroundImage渲染后成为 ` background-image`; - 可以不用写
px直接采用数字1取代1px,React 会自动加上px,有些 CSS 样式属性不会自动加上px,请参考不会地洞添加 px 的样式属性;WebkitTransition和msTransition中,Webkit和ms - 是 JS前缀(JavaScript prefix),解决跨平台,更多参考Modernizr Prefixed;
The style attribute accepts a JavaScript object with camelCased properties rather than a CSS string. This is consistent with the DOM style JavaScript property, is more efficient, and prevents XSS security holes.
from DOM Differences, React
React Native 对比 iOS & Android(beta)
- iOS 和 Android 的 UI 都基于类 XML 形式的,React Native 在
- 组件的事件应该自己响应。
举个栗子:React 中使用 JS 实现 CSS 能力
例如:使用 JS 实现 :hover, :focus, and :active:
方式一,
使用 JS 库,以Radium 为例,其他组件不再赘述:
var styles = {
base: {
background: 'black',
height: 100,
width: 100,
':hover': {
backgroundColor: 'red'
},
':focus': {
backgroundColor: 'green'
},
':active': {
backgroundColor: 'yellow'
}
}
};
方式二,
在 React 组件中添加 this.state.hovered, 当 state 中的 hovered 值改变的时候,组件就进行重绘。implement a:hover
<button style={m(
this.styles.container,
this.state.hovered && this.styles.hover,
)}>{this.props.children}</button>
m() 函数用于合并 style 样式,类似:
m = () => {
let res = {};
for(let i = 0; i < arguments.length; ++ i) {
if(arguments[i]) {
Object.assign(res, arguments[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
方式三,
使用 onMouseEnter 和 onMouseLeave 实现。
var Link = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function(){
return {hover: false}
},
toggleHover: function(){
this.setState({hover: !this.state.hover})
},
render: function() {
var linkStyle;
if (this.state.hover) {
linkStyle = {backgroundColor: 'red'}
} else {
linkStyle = {backgroundColor: 'blue'}
}
return(
<div>
<a style={linkStyle} onMouseEnter={this.toggleHover} onMouseLeave={this.toggleHover}>Link</a>
</div>
)
}
再举个栗子
JS 中实现伪元素(pseudo element) :before & :after
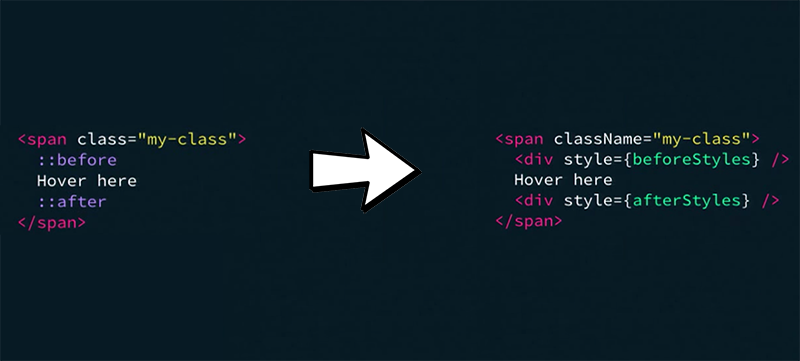
W3C 对于 Inline Style 的支持与说明:
Inline Style 不能实现 keyframe:Inline Style 识别 animation-name 去找对应的 animation 定义然后执行,也不能把 animation 定义对象 写在 Inline Style 中。
The ‘animation-name’ property defines a list of animations that apply. Each name is used to select the keyframe at-rule that provides the property values for the animation. If the name does not match any keyframe at-rule, there are no properties to be animated and the animation will not execute. from CSS Animations, W3C.
不能在 Inline Style 中使用伪类(pseudo classes):
2002年的W3C起草的文档: yntax of CSS rules in HTML’s “style” attribute有提出:
<!-- 浏览器不能识别,会把{...} 当作一个 {object}-->
<p style="{color: #090; line-height: 1.2}
::first-letter {color: #900}"></p>
<!-- 浏览器不能识别,会把{...} 当作一个 {object}-->
<a href="http://www.w3.org/"
style="{color: #900}
:link {background: #ff0}
:visited {background: #fff}
:hover {outline: thin red solid}
:active {background: #00f}">...</a>
如果是这样的话,就好办多了。但在2013年的W3C最新的建议文档中,并没有提供相关的写法: CSS Style Attributes 。
最后,CSS in JS 有足够巨大的想象空间… 在要采用 CSS in JS 的解决方案之时,要三思,天马行空之时,勿忘脚踏实地,兴许那是南柯一梦!
参考:
- Inline CSS styles in React: how to implement a:hover?
- Inline Styles in JS with support for React, Redux, React Native, Autoprefixing, Hover, Pseudo-Elements & Media Queries
- Refactor CSS into Javascript #30
- React Inline Styles are Fundamentally Flawed
- Modular CSS with React
- React: CSS in JS(Stats: 753,383 Views)
- React.js inline style best practices